By leveraging theories and methodologies in computer vision, machine learning, and medical imaging, the research at Health-X aims to help improve the accuracy and efficiency of clinical diagnoses and medical procedures. The applications include neurodegenerative conditions (e.g., Parkinson's disease), neurovascular diseases, brain cancer, and musculoskeletal disorders.
Computational modelling of anatomy and diseases
|
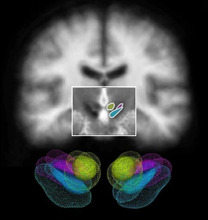
Various diseases and natural aging can result in characteristic alternations to the anatomy and biological tissue properties (e.g, cellular degeneration). With medical imaging data, such as MRI, we want to capture these insights and employ computational models to understand and predict their impacts and progression for the patients. This will be instrumental for the management of diseases and testing new treatments.
|
Immersive & Augmented surgical technology
|
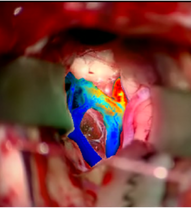
Current and future surgical planning requires the integration of an increasing amount of imaging data and cross-disciplinary expert opinions. This is especially true for neurosurgery, where new brain connectivity data (e.g., tractography) and neural implants are set to transform the paradigm for optimal therapeutic benefits, but further complicate surgical planning. We want to explore novel methodologies (e.g, augmented/virtual reality and signal processing) to facilitate the planning and monitoring of medical procedures.
|
Interactive radiological learning
|
Various human factors can affect the quality of clinical diagnosis and procedures, especially when it comes to perceiving and interpreting medical scans. Although machine/deep learning techniques have shown great potential in radiological applications, the future of computer-assisted diagnosis and procedures can greatly benefit from a user-centered design involving interaction of clinicians and the machine in the clinic.
|